Describe a Major Method That Carbon Is Cycled.
The water cycle takes place on above and below Earths surface. Because some carbon gases are greenhouse gases changes in the carbon cycle that put more carbon in the atmosphere also warm Earths climate.
What Is The Carbon Cycle What Is The Science Behind It United States Carbon Cycle Science Program
Carbon can be stored in a variety of reservoirs including plants and animals which is why they are considered carbon life forms.

. The main abiotic components are air water soil. The biological pump plays a major role in. Burning organic material such as fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide.
The carbon cycle can be described as the exchange of carbon between the land the oceans the atmosphere and the Earths interior. Plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to make their own food. The acid dissolves rocksa process called chemical weatheringand releases calcium magnesium potassium or sodium ions.
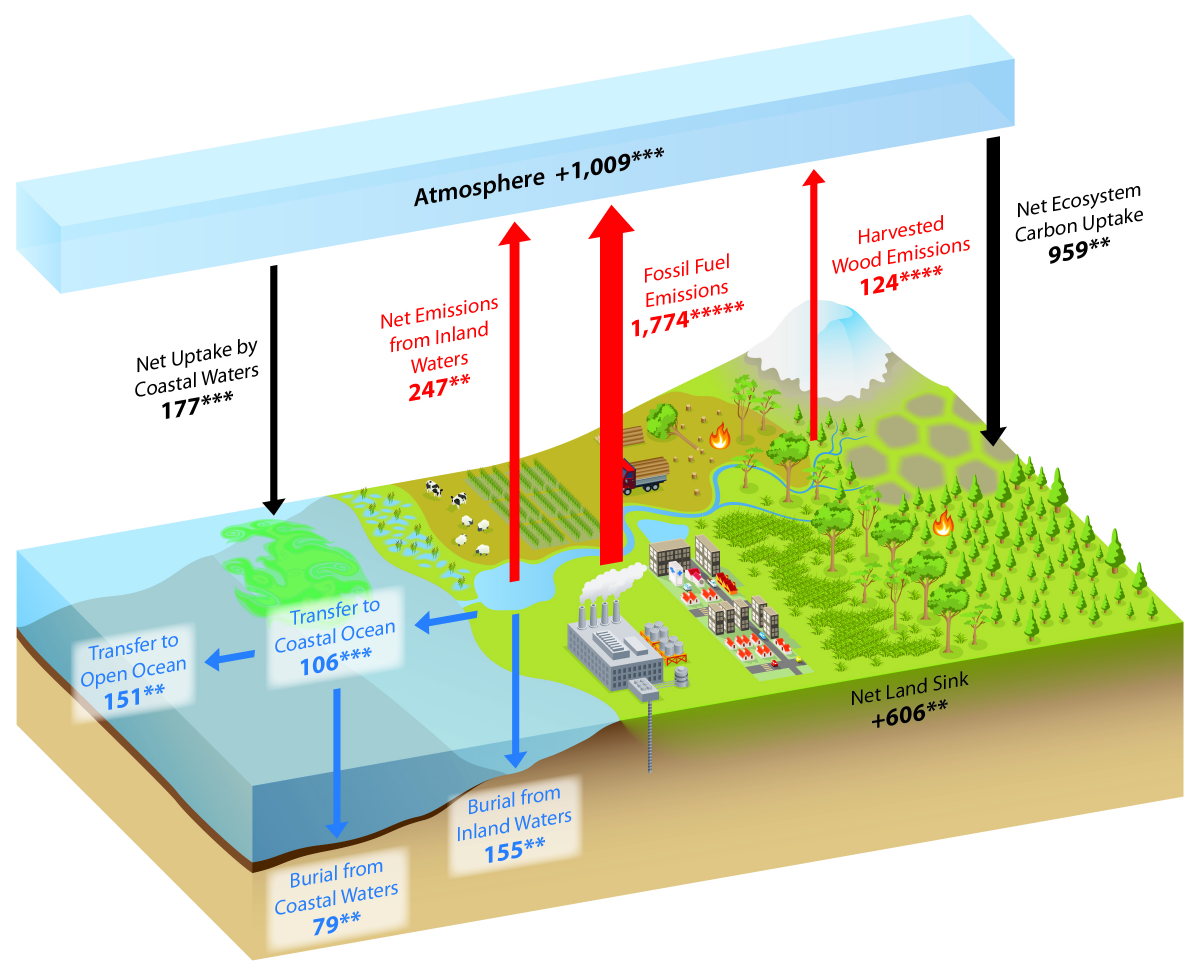
Moving carbon throughout the ocean. This graph known as the Keeling Curve shows how atmospheric CO 2 has continued rising since then. Increased carbon in the atmosphere contributes to the.
The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle. Transforming carbon compounds into new forms of carbon compounds. It not only dissolves directly into the oceans but is utilized by plants in a process called photosynthesis.
The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere. The two processes of the carbon cycle are photosynthesis and cellular respiration. The sun heats the water and gives water molecules enough energy to escape into the atmosphere.
Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration and combustion. In the atmosphere carbon is attached to some oxygen in a gas called carbon dioxide. Atmospheric carbon combines with water to form a weak acidcarbonic acidthat falls to the surface in rain.
Are recycled mainly in soil and are available locally. Just like the terrestrial carbon cycle the oceanic biological carbon pump is all about photosynthesizing respiring eating producing waste products dying and decomposing. Carbon is used by plants to build leaves and stems which are then digested by animals and used for cellular growth.
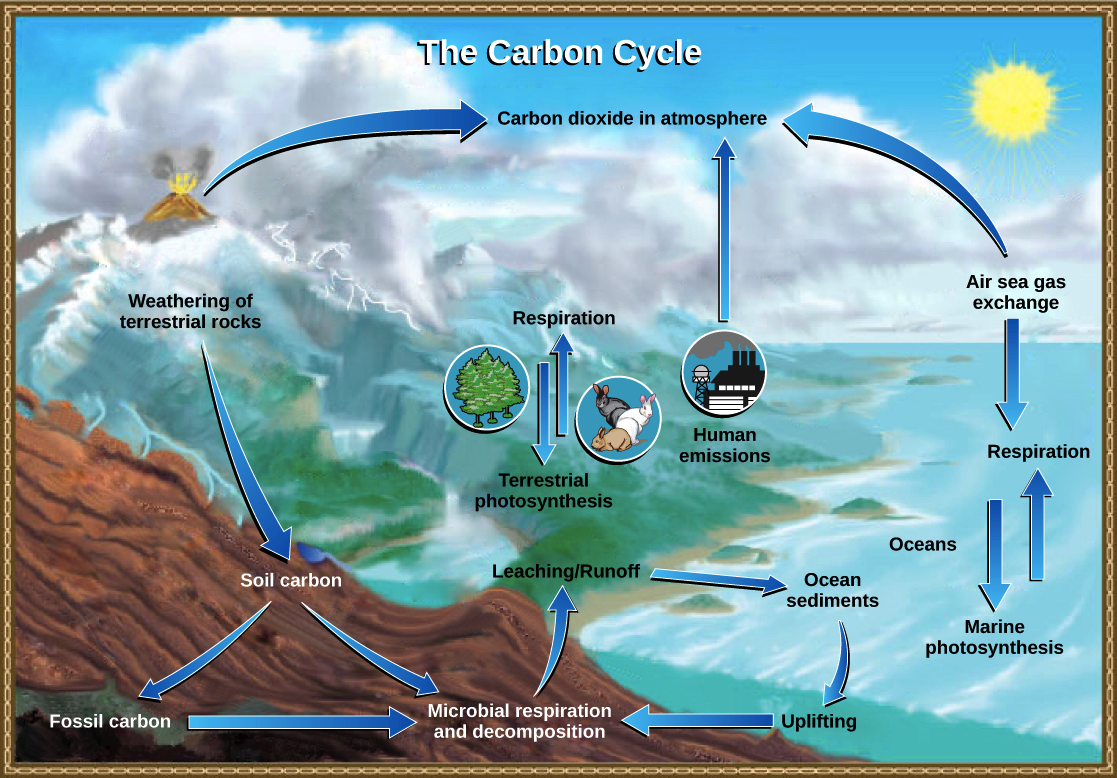
The ocean plays a critical role in carbon storage as it holds about 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere. It is on the move. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land ocean and life through biological chemical geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle.
On the short time scale the carbon cycle is most. The slow carbon cycle involves medium to long-term geochemical processes belonging to the rock cycle see diagram on the right. Intro to biogeochemical cycles.
It is one of the faster components of the planets overall carbon cycle supporting the exchange of more than 200 billion tons of carbon in and out of the atmosphere throughout the course of. Some of this carbon is transferred to soil as plants die and decompose. In the cycle water occurs as water vapor liquid water and ice.
Fossil fuels such as coal petroleum products and natural gas are sources of ancient biomass that were formed millions of years ago from the decay of plant and animal matter. Respiration excretion and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil continuing the cycle. Processes involved in the carbon cycle are.
The 4 main nutrient cycles are. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere or on Earth is constantly in flux. The atmospheric carbon cycle accounts for the exchange of gaseous carbon compounds primarily carbon dioxide between Earths atmosphere the oceans and the terrestrial biosphere.
The exchange between the ocean and atmosphere can take centuries and the weathering of rocks can take. There are also exchanges with the ocean which are only hinted at here. It is one method of reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere with the goal of reducing global climate change.
Nutrient recycling involves both biotic and abiotic components. Carbon cycles far more slowly through geological processes such as sedimentation. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers to make glucose in photosynthesis.
Recycling of Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen and Oxygen occurs in water air and soil whereas calcium phosphorus potassium etc. Carbon may be stored in sedimentary rock for millions of years. Because the Earth is a dynamic place carbon does not stay still.
In photosynthesis carbon from carbon dioxide is fixed into carbohydrates. All living things are made of carbon. The oceans are a major carbon storage system for.
Plants grab carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to use in photosynthesis. This depiction of the carbon cycle focusses on the terrestrial land-based part of the cycle. Starting in 1958 Charles Keeling used the scientific method to take meticulous measurements of atmospheric carbon dioxide CO 2 at Mauna Loa Observatory in Waimea Hawaii.
Evaporation occurs when water on the surface changes to water vapor. Carbon is also a part of the ocean air and even rocks. Note that carbon atoms are incorporated.
Animals that eat plants digest the sugar molecules to get energy for their bodies. In the cycle anything storing more carbon that it releases is called a carbon sink. Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide.
The cycle starts with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The reactions of the fast carbon cycle to human activities will determine many of the more immediate impacts of climate change. This process occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
A carbon source is any-thing releasing more carbon than it absorbs. The movement of carbon from the atmosphere to the lithosphere rocks begins with rain. Burning of fossil fuels such as oil releases carbon into the atmosphere.
This carbon must be cycled - removed from the atmosphere - back into living organisms or it stays in the atmosphere. This fairly basic carbon cycle diagram shows how carbon atoms flow between various reservoirs in the Earth system. Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment the amount of carbon in this system does not change.
When volcanoes erupt they give off carbon dioxide that is stored in the mantle. Learn how carbon moves through Earths ecosystems and how human activities are altering the carbon cycle. Photosynthesis plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and form it into sugar starch and other organic compounds.
The USGS is conducting assessments on two major types of carbon sequestration.

Carbon Cycle Diagram Center For Science Education

Carbon Cycle And Its Working Carbon Cycle Cool Science Facts Ap Environmental Science
No comments for "Describe a Major Method That Carbon Is Cycled."
Post a Comment